| CATEGORY: | Research |
| CSA PROJECT: | Climate-Smart Villages |
| SCALE: | National & County |
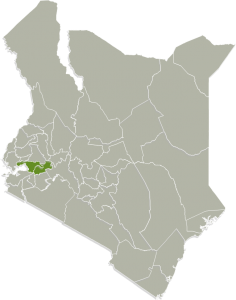
| LOCATION (COUNTY) | Kisumu and Kericho |
| PERIOD OF THE PROJECT: | 2011 – 2021 |
| GRANT SIZE OF THE PROJECT: | N/A |
CCAFS CSA
Summary of Actions
The CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security in East Africa (CCAFS EA) seeks to support the countries in East Africa such as Kenya, in their pursuits to achieve sustainable developmental goals as well as fulfill national, regional and international climate-related commitments. To achieve this, CCAFS EA is promoting climate-smart agriculture (CSA)—a strategic approach to agriculture that aims to solve the region’s increasing developmental and climate-related challenges by introducing climate-smart practices and technologies to sustainably increase agricultural productivity and income, enhance resilience and adaptive capacity, while reducing emissions and sequestering carbon.
Context
The agricultural sector in Kenya is the largest contributor of Kenya’s GDP. The key challenges for the sector is overreliance on rain fed agriculture, and extreme weather events such as drought and flood. In order to build resilience in agricultural systems within Kenya, CCAFS promotes innovations by tapping into the expertise of other CGIAR Centers, as well as other national and regional research networks. Efforts are focused around the promotion of climate-smart agriculture that facilitates adaptation and mitigation in cereal-based and livestock systems. CCAFS EA has established research sites to introduce, test, evaluate and promote technological and institutional CSA options for addressing climate variability and change in agriculture. These sites have been established as Climate-Smart Villages (CSVs), and act as ‘lighthouses’, allowing communities to test, co-develop and adopt integrated portfolios of CSA practices.
Objective
CCAFS EA aims to contribute to a climate-resilient East Africa, which is food and nutrition secure and that has equitable access to livelihood opportunities for all. Complementary objectives that support these goals include: increasing carbon storage in agricultural systems, reducing GHG emissions from food systems and agricultural value chains, supporting enabling policies and increased investments in agriculture and natural resource management.
Key Interventions
| FARM LEVEL | TARGET(NO OF FARMERS) | INDICATORS MONITORED |
| Climate smart agriculture practices | Farmers, research & development partners, value-chain actors | Number of site-specific targeted CSA technologies or practices implemented. |
| Access to climate services | Farmers | Number of farmers accessing climate information services for decision making |
| BEYOND FARM LEVEL | TARGET BENEFICIARIES | INDICATORS MONITORED |
| Policy and advocacy
|
Policy makers | Number of policy decisions and strategies taken (in part) based on CCAFS science and knowledge products
Number of institutions and major initiatives using CCAFS outputs for services helping farm households manage climate risks |
| Inclusion of youth and women in climate smart agriculture practices | Research & development partners | Number of organizations adapting plans to increase women’s access to decision making and control over resources |
Participation In Key Climate &Agriculture Networks
CCAFS is a member of: Climate Smart Agriculture Multi-stakeholder Platform; African Group of Negotiators-Expert Support (AGNES) and Africa Climate Smart Agriculture Alliance (ACSAA).
Involvement In CSA
Relevance of CSA MSP to Work
- Research
- Policy formulation
- Knowledge dissemination
- Coordination and networking
- Technology transfer
- Information about CSA
- Networking
- Learning and exchange
- Reporting and showcasing
- Influence policy environment
Recommendation On Ways To Support MSP
- Developing specific climate smart agriculture policies, legislations, strategies, plans,
- Dissemination of climate smart agriculture knowledge and technologies
- Capacity building of key actors involved in climate smart agriculture implementation
- Mobilizing actors and facilitating dialogue on climate smart agriculture issues/actions
- Conduct research to provide scientific evidence
Lessons Learned/Challenges In CSA Project Implementation
Collective action groups are important platforms for innovative partnerships that provide new knowledge and skills and build the capacity of local farmers to change farming practices while adopting new crop and livestock interventions. They empower members to pool financial resources for savings, provide labor for farm operations, and make it easier to provide agro-advisory services and farm inputs of good quality at affordable prices.
Up scaling and out scaling of CSA technologies and practices, will require the strengthening of enabling conditions such as climate information, agro-advisories and access to finance and strengthening existing farmer experimentation networks including mobilizing farmers to continue working in groups. Moving forward, resource poor vulnerable farmers, women and youth should be at the center of efforts to build adaptive capacity.
Organisation Information and Contact Address in case of Follow Up
Name: John Recha
Email address: j.recha@cgiar.org
Phone address: +254 20 422 3449
Organisational Physical address: International Livestock Research Institute Campus, Uthiru, Nairobi
Organisational Website: https://ccafs.cgiar.org/